How to choose a validator
All validators have the same base reward, which depends only on the network's general parameters. However, each validator offers different conditions for delegators. Therefore, analyze all the data, study the information about the validator to make a decision about delegation.
Go to the Decimal Explorer at https://explorer.decimalchain.com, click Blockchain menu, and select Validators:
Here you see the number of validators:
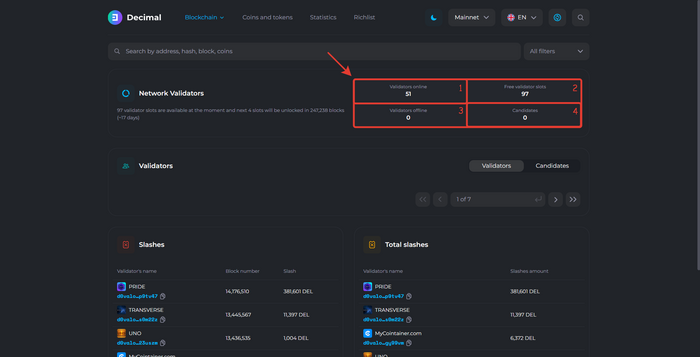
- 1. Validators online. The number of authorized validators that are online.
- 2. Free validator slots. Available slots for connecting validators.
- 3. Validators offline. The number of disconnected validators.
- 4. Candidates The number of authorized validators that are currently offline and not signing blockchain blocks.
Below on the page, you will find the following blocks:
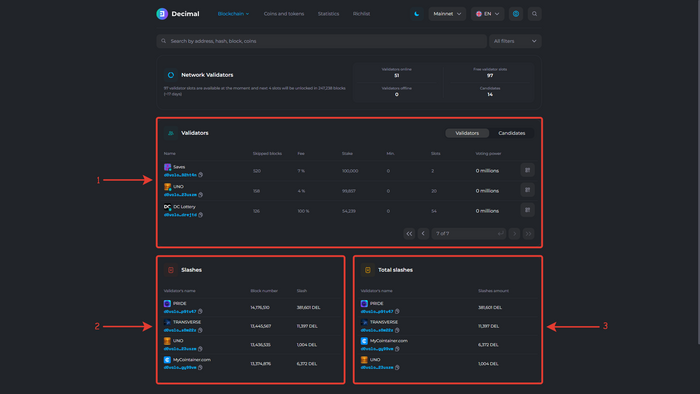
1. Validators. The block with online validators.
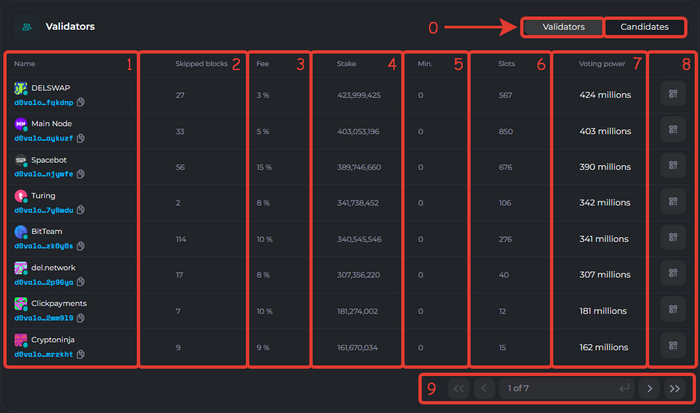
- Validators / Candidates Tab
- 1. Name. The name of the validator and the public key can be copied by clicking on the button next to the address. If you send coins to this address (public key), they will be delegated.
- 2. Skipped blocks. The number of missed blocks that the validator did not sign.
- 3. Fee.The commission that is set once when creating a validator. The validator deducts this commission from the rewards of the users who delegated their coins to the selected validator.
- For example, if the commission is 6%, then out of 100 coins that the blockchain pays you for the delegation transaction, you receive 94 coins (100 coins - 6%).
- For example, if the commission is 6%, then out of 100 coins that the blockchain pays you for the delegation transaction, you receive 94 coins (100 coins - 6%).
- 4. Stake. The total number of coins that the validator has in delegation (own stake + delegator stakes).
- 5. Min. The minimum number of coins that can be delegated to the selected validator.
- For example, if the validator has a minimum stake of 100 DEL, and you delegate 101 DEL, then the last delegating user who has 100 DEL stops being a delegator, and their coins are returned (in this case 100 DEL).
- For example, if the validator has a minimum stake of 100 DEL, and you delegate 101 DEL, then the last delegating user who has 100 DEL stops being a delegator, and their coins are returned (in this case 100 DEL).
- 6. Slots. The number of occupied delegation slots. The maximum number of slots is 1000.
- For example, if all 1000 slots are occupied, it is possible to "outbid" the minimum stake by delegating more coins than the smallest stake. Thus, the user with the smallest stake stops being a delegator, and their coins are returned.
- For example, if all 1000 slots are occupied, it is possible to "outbid" the minimum stake by delegating more coins than the smallest stake. Thus, the user with the smallest stake stops being a delegator, and their coins are returned.
- 7. Voting Power. The total stake displayed but rounded to show the weight of the validator when voting, which will be available in the DAO.
- 8. QR-code. Allows scanning the validator's public key to send funds to it for delegation.
- 9. Navigation field between pages.
2. Penalties. This block shows the penalties that validators and their delegators received. A penalty is the removal of coins from the total stake of delegators and the validator from 1 to 5% and their immediate burning.
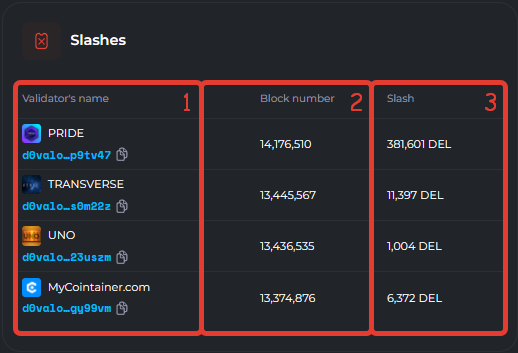
- 1. Validator`s name. The name of the validator and the public key with a copy button.
- 2. Block number. The number of the block in which the validator was penalized.
- 3. Slash The number of coins that the validator and delegators were penalized. The penalty is distributed among all participants (validator and delegators) in proportion to their stake.
3. Total penalties. This block shows the total sum of all penalties that the validator received over time.
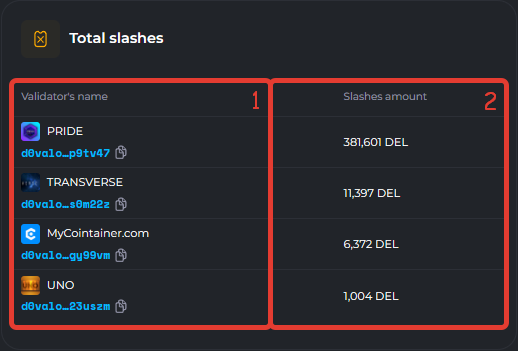
- 1. Validator`s name. The name of the validator and the public key with a copy button.
- 2. Slashes amount. The sum of all penalties that the validator received over time after updating the blockchain to the Decimal Smart Chain version.